what are 5 examples of monosaccharides Monosaccharide monosaccharides give example atoms carbons number many hillis2e pentose disaccharide varying numbers kind same figure made ch02
Carbohydrates are one of the most essential and abundant classes of biomolecules found in nature. These molecules are made up of simple sugar monomers that are linked together in different arrangements to form complex structures. One of the most widely known functions of carbohydrates is their role as a source of energy for living organisms. When carbohydrates are ingested, they are broken down into simple sugars such as glucose and fructose, which can be easily converted into energy by cellular respiration. In addition to providing energy, carbohydrates also play an important role in the formation of structural molecules such as cell walls, which provide support and protection for cells. There are several different types of carbohydrates, ranging from simple sugars such as glucose and fructose to complex carbohydrates such as starch and cellulose. Monosaccharides, or simple sugars, are the building blocks of all carbohydrates. They have the general formula (CH2O)n, where n can range from three to seven. The most common monosaccharides include glucose, fructose, and galactose. The next level of carbohydrate complexity is disaccharides, which are formed when two monosaccharides are linked together. Common disaccharides include lactose, which is composed of glucose and galactose, and sucrose, which is composed of glucose and fructose. Moving up the complexity ladder, polysaccharides are formed when many monosaccharides are linked together. Starch and glycogen are both examples of polysaccharides that are used by organisms to store energy. In plants, starch is the primary energy storage molecule, while in animals, glycogen serves the same purpose. Another important polysaccharide is cellulose, which forms the structural component of plant cell walls. Cellulose is unique because humans and other animals lack the necessary enzymes to digest it, making it an important source of dietary fiber. In conclusion, carbohydrates are a crucial class of biomolecules that are involved in providing energy and structural support for living organisms. From simple sugars to complex polysaccharides, they come in a variety of forms and serve a multitude of functions. Understanding the different types of carbohydrates and how they are utilized by living organisms is crucial for understanding the basic principles of biochemistry.
If you are looking for Carbohydrates - Monosaccharides, Disaccharides, Polysaccharides you’ve came to the right page. We have 5 Pics about Carbohydrates - Monosaccharides, Disaccharides, Polysaccharides like 7.2: Carbohydrates - Biology LibreTexts, Carbohydrates - Monosaccharides, Disaccharides, Polysaccharides and also hillis2e_ch02. Here you go:
Carbohydrates - Monosaccharides, Disaccharides, Polysaccharides
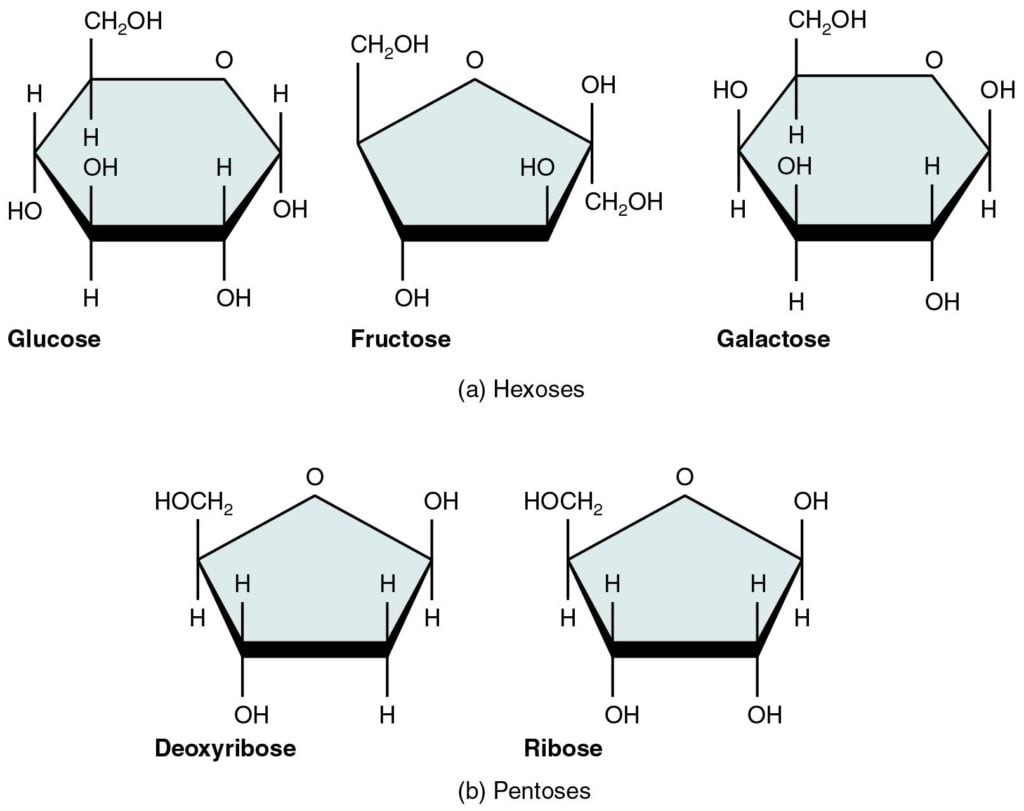 microbenotes.commonosaccharides carbohydrates polysaccharides structure examples simple disaccharides properties which sugars there carbon
microbenotes.commonosaccharides carbohydrates polysaccharides structure examples simple disaccharides properties which sugars there carbon
Hillis2e_ch02
 www.macmillanhighered.commonosaccharide monosaccharides give example atoms carbons number many hillis2e pentose disaccharide varying numbers kind same figure made ch02
www.macmillanhighered.commonosaccharide monosaccharides give example atoms carbons number many hillis2e pentose disaccharide varying numbers kind same figure made ch02
Chapter 11 : Carbohydrates | Mcat Study, Biochemistry, Study Tools
 www.pinterest.commonosaccharides examples some table ketoses aldoses study atoms biochemistry cn bioinfo quora mcat
www.pinterest.commonosaccharides examples some table ketoses aldoses study atoms biochemistry cn bioinfo quora mcat
7.2: Carbohydrates - Biology LibreTexts
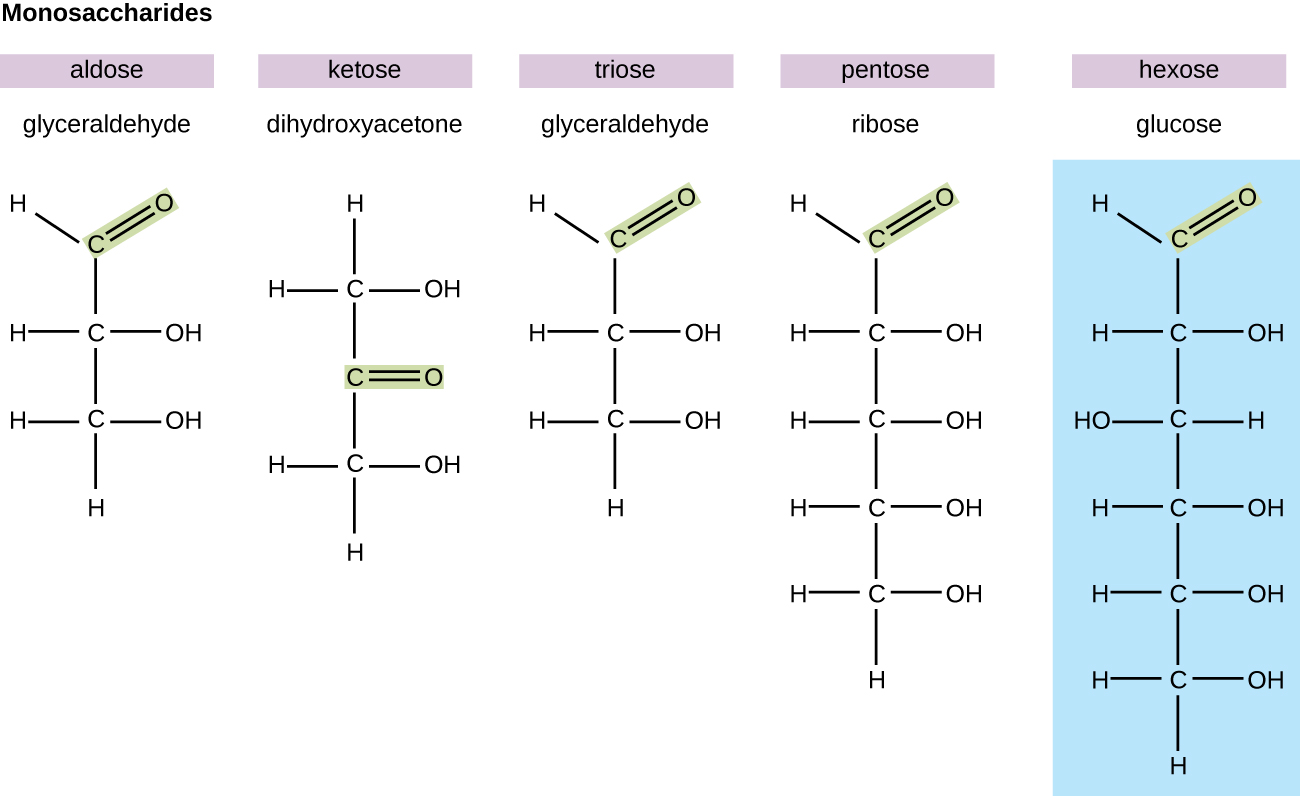 bio.libretexts.orgmonosaccharides carbohydrates carbons group carbonyl number based figure aldose carbon ketose hexose chain glucose triose pentose glyceraldehyde double classified backbone
bio.libretexts.orgmonosaccharides carbohydrates carbons group carbonyl number based figure aldose carbon ketose hexose chain glucose triose pentose glyceraldehyde double classified backbone
Monosaccharides (Simple Sugars) Definition, List, Examples Of Foods
 www.pinterest.commonosaccharides sugars carbohydrates monosaccharide fructose galactose disaccharide carbons glucose carbohydrate types polysaccharide mono karbohidrat sucre chemicals macronutrients carbs absorption monosakarida
www.pinterest.commonosaccharides sugars carbohydrates monosaccharide fructose galactose disaccharide carbons glucose carbohydrate types polysaccharide mono karbohidrat sucre chemicals macronutrients carbs absorption monosakarida
Hillis2e_ch02. Monosaccharides sugars carbohydrates monosaccharide fructose galactose disaccharide carbons glucose carbohydrate types polysaccharide mono karbohidrat sucre chemicals macronutrients carbs absorption monosakarida. Monosaccharides carbohydrates carbons group carbonyl number based figure aldose carbon ketose hexose chain glucose triose pentose glyceraldehyde double classified backbone